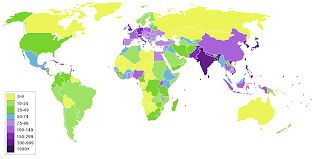
The main waves of migration were migrations of the world to America.
People of central and northern Europe emigrated to South America, and then, they went to Canada and to the EEUU but some people stayed here (in Argentina, Brazil...). People from Spain emigrated to America specially during and after the war in our country (you can see it on the map).
People of central and northern Europe emigrated to South America, and then, they went to Canada and to the EEUU but some people stayed here (in Argentina, Brazil...). People from Spain emigrated to America specially during and after the war in our country (you can see it on the map).